In the age of technological surge, nothing exemplifies modern ingenuity like 3D printing does. Simultaneously ingenious and futuristic, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is cutting a path towards a transformative revolution. Its possibilities are constantly expanding, promising a 3D printing future that could change the very fabric of manufacturing, distribution, and consumption. In order to fully appreciate this futuristic technology we will dive into what 3D printing is, how does 3D printing work, and explore the potential real-world 3D printing applications.
Untangling the Enigma of 3D Printing
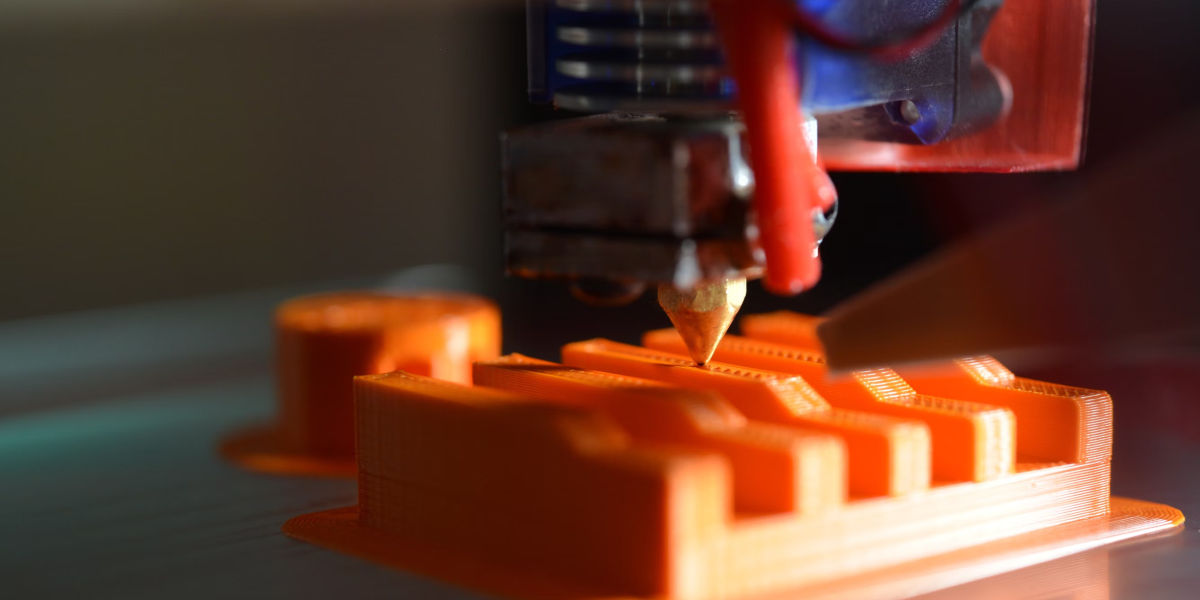
Before we dig deeper into the 3D printing future, let's first understand what it is. Put simply, 3D printing is a process where physical objects are created from a digital blueprint. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that remove material through carving or drilling, 3D printing is an additive process, which means it adds layers of materials to build objects - hence why it's also known as additive manufacturing.
The 3D printing technology uses a range of materials from plastics to metal alloys, and everything in between. Upon receiving the design blueprint, the 3D printer deposits material layer after layer, in precise geometric shapes to form the final product. Each layer works as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the actual object, coming together to create a solid three-dimensional object.
Decoding the Mechanism: How Does 3D Printing Work?
The process of 3D printing may seem relatively ësimpleí on the surface, yet it actively involves a multitude of steps, each requiring its own sublevel of sophisticated engineering. To start, one needs a blueprint or a digital 3D model. This can either be created from scratch on computer-aided design (CAD) software or scanned into the computer from an existing object.
Once the design is ready, it is sliced into hundreds, or sometimes even thousands, of horizontal layers. This step prepares the design for the printer to understand and build layer by layer. After that, it is simply a matter of sending the file to the printer and watching the magic unfold. The printer reads each slice from the digital file and deposits materials corresponding to each layer, gradually building the object.
The Next Chapter: Future of 3D Printing
Arguably one of the most exciting things about 3D printing is its seemingly limitless potential. Not only does 3D printing hold the promise of completely transforming traditional manufacturing processes, but it could also forever change sectors like healthcare, food production, and even space travel. Though we are still in the early stages of fully realizing the capabilities of 3D printing, the 3D printing future certainly shines brightly.
Moving on to another fascinating aspect of the future of 3D printing, let's delve a little deeper into particular applications that might revolutionize specific industries. The implications are indeed far-reaching and quite promising.
A New Dimension in The Medical Industry
One of the most significant applications of 3D printing lies in the medical industry. Bio-printing, which refers to 3D printing of body parts, is now becoming a frontier in medical science. Researchers are working tirelessly to create functional organs, like the liver and kidneys, using a patient's cells. This process reduces the need for organ donations and the risk of the body rejecting the new organ. While still early in development, there is no doubt that bioprinting will change the face of healthcare as we know it.
Revolutionizing The Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing sector, 3D printing brings about an incredible level of customization. Companies can produce parts to precise specifications and in small quantities if needed. This technology, also known as additive manufacturing, serves as a cost-effective tool for creating complex geometries that would be difficult or even impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
Environmentally Friendly Construction
3D printing also carries potential applications in sustainable and fast construction. Companies are now creating 3D-printed houses that take less time to build and generate less waste. These eco-friendly homes could prove essential in addressing housing crises in various parts of the world.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Now that we've explored various applications of 3D printing, it's important to understand its underlying mechanism. 3D printers use digital models and turn them into real, physical objects. The process involves building the item layer by layer - a stark contrast from traditional manufacturing processes that often involve cutting out and hollowing a piece from a bigger block.
Firstly, you must create a 3D blueprint using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The software then splits the digital model into hundreds or thousands of horizontal layers. These slices guide the 3D printer, allowing it to build the model from the ground up, layer by layer.
Most 3D printers today use a method known as Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM). The printer melts a filament material (like plastic) and deposits it layer by layer following the 3D designs until the object is complete. Other techniques include Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which involve the use of liquid resin or powder, respectively.
From creating organs and customized manufacturing parts to constructing eco-friendly homes, the future of 3D printing certainly stands laced with potential. As we continue to strengthen and refine this technology, who knows the bounds we may surpass?