Imagine you could see all the forces at work around you, not just gravity pulling you towards the earth, but also the forces that allow your smartphone to connect to Wi-Fi, light up a light bulb, or the force that keeps the atoms in your body intact. One such invisible force is Electromagnetism. This article will delve into the realms of understanding Electromagnetism, its correlation with the four fundamental forces, and why it holds such paramount significance in our everyday lives and the field of physics.
Understanding Electromagnetism: The Second of The Four Fundamental Forces
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, and the second on the list after gravity. This invisible force governs how atoms interact and how light behaves, encompassing a wide spectrum of phenomena - from static electricity to the dazzling spectacle of northern lights in the sky.
The other three fundamental forces include— gravity, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. Unlike gravity, which acts at long distances, and the nuclear forces that work at micro-levels, Electromagnetism operates on an intermediate scale. As scientists continuously delve deeper into this intriguing phenomenon, understanding Electromagnetism unravels compelling insights into the world we live in.
The Phenomenal Journey of Understanding Electromagnetism
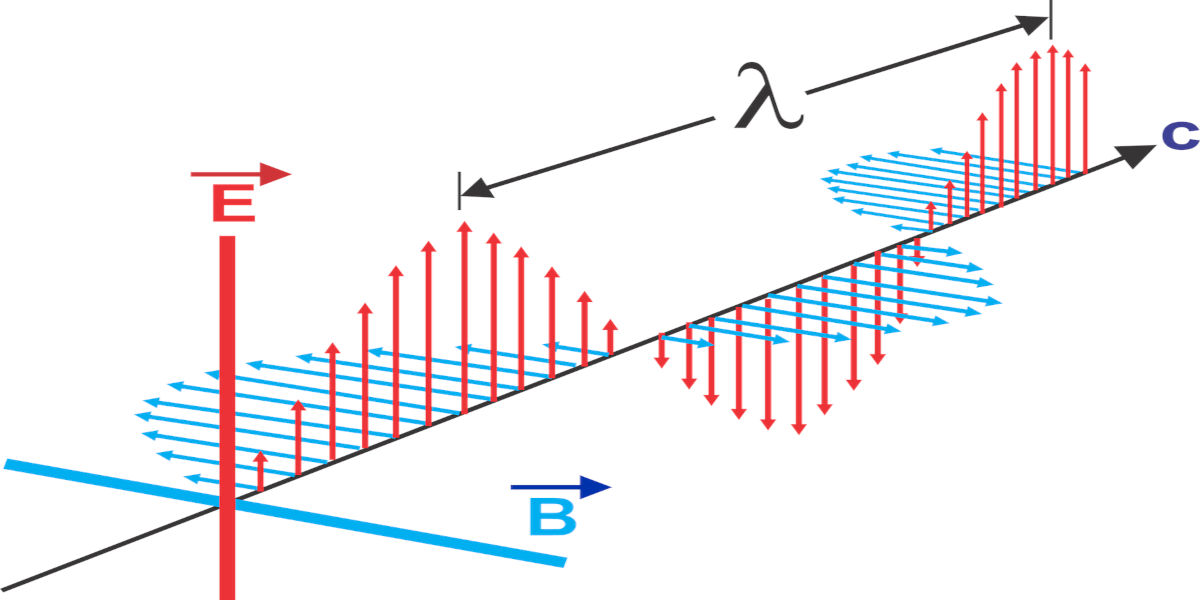
Historically, electricity and magnetism were studied as separate entities. It was only in the 19th century when physicist James Clerk Maxwell formulated the electromagnetic theory did we understand that both are sides of the same coin – two related aspects of a single overarching phenomenon known as Electromagnetism.
Maxwell's equations were groundbreaking, as they helped articulate how changing electric fields can generate magnetic fields, and vice versa, thereby setting forth the foundation of modern electromagnetic theory. Since then, the conceptual understanding of Electromagnetism has shaped many technological advancements and scientific theories.
Why is Electromagnetism So Important?
Electromagnetism's relevance is ubiquitous, encompassing various facets of our everyday life and the scientific world around us. Let's explore why this invisible force is so crucial.
First, Electromagnetism is responsible for the force between charged particles which ultimately culminates in the structure of atoms. Therefore, the world as we know it depends on electromagnetic forces. Without it, atoms wouldn't come together to create the earth, water, air, or even life itself.
Secondly, Electromagnetism plays a crucial role in the technology we use every day. Whether it is the operation of electronic devices, communication systems, or electric motors — Electromagnetism is at the core. Understanding this force has allowed us to harness its power, leading to revolutions in technology and industry.
In physics, Electromagnetism is vital as it bridges the gap between the macroscopic world of gravity-based astronomy and the microscopic realm of quantum mechanics. It acts as a perfect link, providing a unifying force that allows researchers to have a more cohesive understanding of the universe and its laws.
Electromagnetism is an invisible yet indisputably powerful force that exists in our world. Much of modern technology - be it something as common as a smartphone or as complex as the Large Hadron Collider, owes its existence to our understanding, and hence, usage of electromagnetism. As such, it becomes vital for us to delve deeper into this unseen force and gain a better understanding of its awe-inspiring power.
Fundamentally, electromagnetism refers to the interaction of electrically charged particles. This interaction imparts a force upon these particles, resulting in their movement. It is this movement, or more precisely, the control of this movement, that enables us to create and use electronic devices that have revolutionized our lives. But understanding and manipulation of electromagnetism is a feat that has required decades of physics explorations and breakthroughs.
Unifying Theories and Key Discoveries
One of the key breakthroughs came when physicist James Clerk Maxwell unified the work of his predecessors in his set of equations, now known as the Maxwell’s Equations. They provided a comprehensive mathematical interpretation of how electric and magnetic fields interact with each other and with electric charges and currents. This unification offered a theoretical framework, a guidebook, which scientists and engineers have used to harness the power of electromagnetism.
Another significant development was Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity, where he incorporated Maxwell's equations to relate the laws of electromagnetism with the laws of mechanics under a single framework. This enlarged our understanding of the universe, with electromagnetism being one of the foundational pillars. Hence, the topics of electromagnetism also carry implications far beyond technology, extending into our understanding of reality itself.
The Application of Electromagnetism
From powering our homes and factories, transmitting information across continents, to observing galaxies far, far away, electromagnetism is hard at work. The principles of electromagnetism lie at the heart of electricity generation in power plants. It allows us to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy which can then be conveniently transmitted across vast distances.
The same principles also allow us to communicate, be it via radio waves or fiber optic cables. Electromagnetism facilitates the transmission and reception of signals - a crucial aspect of communication technologies. MRI scanners, a marvel of medical imaging, function due to the interaction of electromagnetic fields with the human body.
Looking away from Earth, our grasp over electromagnetism enables us to peer across vast distances in the universe. Radio telescopes function by receiving electromagnetic radiation from distant celestial bodies, offering us a glimpse into the universe's distant past.
Conclusion
The invisible force that is electromagnetism is a crucial aspect of both our modern technological society and our understanding of the universe. The examples briefed in this article merely scratch the surface of electromagnetism's applications. Its influence and significance will only continue to grow as our knowledge deepens, revealing further dimensions of this fascinating force that invisibly steers so much of our lives and universe.