From the psychedelic mind-scapes of artists to the abstruse formulae of physicists, humankind has always sought novel ways to represent and make sense of the elusive reality we inhabit. One such pioneering approach belongs to the world of quantum physics – an eccentric arena where particles can be at two places at once, become entangled over large distances, and even pop out of the vacuum. And the awe-inspiring tool that enables us to simplify and visualize this quantum field theory is the Feynman Diagrams.
Feynman Diagrams Simplified
Conceived by physicist Richard Feynman, these diagrams have revolutionized the way physicists visualize and conceptualize the interactions in the quantum realm. Unlike sophisticated mathematical representations, these simplified sketches represent the probabilistic behavior of subatomic particles — the quantum-scale actors that constitute the universe.
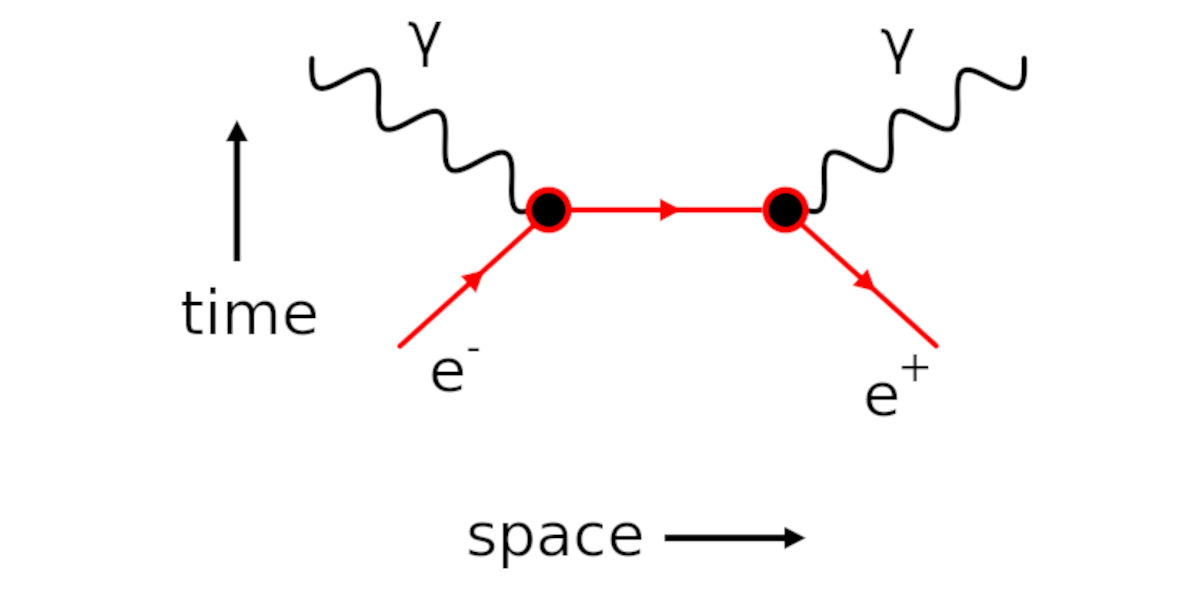
Feynman Diagrams showcase particles as lines moving forward in time, while their interactions are depicted as points where these lines intersect — making it easier for anyone, physicists and novices alike, to get an intuitive grasp of the event. Yet, these feather-light drawings carry profound implications, aiding physicists to decipher complex quantum model computations with ease.
Quantum Field Theory Visualized
Moving beyond the structure of single particles and atoms, the quantum field theory represents the dynamic, interactive universe at a fundamental level. It explicates how particles pop in and out of existence (also termed as virtual particles), how they react to forces, and how distinct particles can sometimes act as waves in a field.
Feynman diagrams serve as the perfect pictorial aid for visualizing these oddball phenomena. They allow us to explore how particles like electrons and photons, or quarks and gluons, interact with each other within the quantum field's framework. By illustrating the connections and sequences of these interactions, they embody the essence of the quantum world's unpredictability and interconnectedness.
What Do Feynman Diagrams Represent?
But what exactly do Feynman Diagrams capture? Each line, each vertex, and each loop in a Feynman diagram depicts vital information about the quantum world. Straight lines represent fermions or matter particles like quarks and electrons. Wavy lines signify bosons — particles which mediate the fundamental forces, like photons for electromagnetic force. The points or vertices where these lines meet represent the interaction between these particles.
Furthermore, time progression in these diagrams is conventionally represented from left to right, demonstrating particle interactions as a series of events. They show us how a high energy electron emits a photon upon getting excited and re-absorbs it, reverting to its low energy state. And all this complex quantum choreography is presented in a single, comprehensible snapshot – the Feynman Diagram.
Even though quantum physics might bewilder us with its peculiar and unintuitive phenomenology, tools like Feynman Diagrams, once understood, provide us with a simplifying lens to perceive and unravel the unimaginable intricacies of the quantum universe. Embracing such innovative visualization techniques, science strives to make the unseeable seen, to unravel the subtleties of nature that are both profoundly beautiful and fundamentally mind-bending.
Digging Deeper into Quantum Field Theory
Quantum Field Theory (QFT) is a complex field of study that offers a detailed examination of the quantum phenomenon. While its mathematical intricacies can be overwhelming for non-specialists, visual tools like Feynman diagrams can simplify our understanding of this elusive quantum world.
Feynman diagrams, first introduced by physicist Richard Feynman in the mid-20th century, are pictorial representations used primarily in the field of quantum electrodynamics (QED) to diagramatically illustrate the behavior of subatomic particles. Using relatively simple drawn lines and vertices, these diagrams provide a visual tool to explain diverse phenomena from elementary particle interactions to the detailed mechanics of quantum transitions.
Each line in a Feynman diagram represents a particle, and the way in which the lines interact represent different particle processes. Lines meeting at a vertex symbolize a particle interaction, while those beginning or ending on their own symbolize creation or annihilation of particles. This color and clarity in visual representation offers a more holistic understanding of abstract quantum concepts.
Feynman Diagrams: A Pictorial Representation
While the beauty of these diagrams lies in their simplicity, the true depth of the Feynman diagrams goes beyond their elementary appearance. Each diagram is not just a pictorial representation, but a visual expression of integrals in the perturbation theory, an approximate description of the quantum world.
In other words, Feynman diagrams represent mathematical expressions associated with a consistent theory of quantum mechanics. A mathematical expression corresponds to each diagram, and the sum of all possible diagrams provides us with quantum corrections to different processes.
Understanding quantum field theory through Feynman diagrams can be likened to deciphering an alien language. Just as we might learn to associate alien symbols with familiar concepts, physicists engage in similar processes when interpreting Feynman diagrams. Once this association is built, one can read Feynman diagrams as sentences in the narrative of particle interactions.
Contributions of Feynman Diagrams
Feynman diagrams have contributed immeasurably to the field of quantum physics. Their elegance lies in the fact that they provide a more intuitive and manageable way to make sense of an otherwise abstract and mathematically complex reality. They act as a bridge between the abstract world of quantum mechanics and the intuitive world of human cognition.
While Feynman diagrams make quantum field theory understandably less intimidating, it's vital to remember that they are just one among various tools available to physicists. As always, a dynamic balance between mathematical rigour and intuitive reasoning is crucial.
Looking Forward
As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the quantum world, Feynman diagrams undoubtedly remain an integral tool in the magic kit of contemporary physicists. They enable us to navigate the strange and beautiful landscape of quantum mechanics. Whether you’re a student trying to grasp the fundamentals, or a professional engaged in trailblazing research, Feynman diagrams are quite simply indispensable.